INHERITANCE:
The process by which characters are transmitted from parents to offspring(child), is called INHERITANCE.
HEREDITY:
The way by which genes transmit traits(a genetically determined characteristic) from parents to offspring is called HEREDITY.
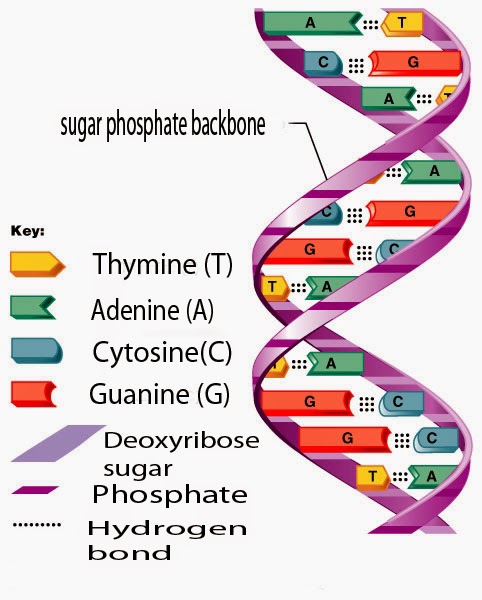
GENE:
The small bodies found on the chromosomes are called GENES. These are the UNITS OF INHERITANCE. Genes take part to transfer one or more characters from parents to the new generation, and responsible for biological expressions i.e. appearance of characters. each gene has a specific function.
For example: A gene determine the height of the pea plants, another gene color of their flower.
LOCUS:
The position of a gene on the chromosomes is called LOCUS.
GENE LOCUS:
The place on the chromosomes where the gene resides is called GENE LOCUS.
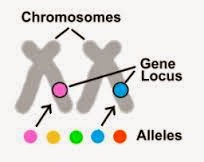
ALLELE:
The alternate form for the same gene is called ALLELE.
For example: All genes controlling a flower color of plant in a similar or dissimilar manner are called ALLELES.
GENOME:
The total amount of genetic material in a total chromosome set of an individual is called GENOME.
KARYOTYPE:
The entire chromosome complement of an individual or cell is called KARYOTYPE.
HYBRID:
The organism that arise from mating between two genetically different parent is called HYBRID.
ALLELOMORPH:
A pair of contrasting characters is called ALLELOMORPH.
For example: Tall and dwarf stem of the plant.
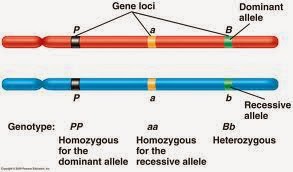
HOMOZYGOUS:
When an individual possesses two alleles controlling a common character in a similar manner then it is called as HOMOZYGOUS.
For example: TT (gene for tallness), RR (gene for red color). Such plants breed true.
HETEROZYGOUS:
An individual is said to be HETEROZYGOUS,if the two members of a pair of genes alleles control a common character in a different manner.
For example: (Tt), (rr).
DOMINANT CHARACTER:
The allele which masks the appearance of other allele in heterozygous condition is said to be DOMINANT CHARACTER.
RECESSIVE CHARACTER:
The allele which is unable to express in heterozygous condition is said to be RECESSIVE CHARACTER.
PHENOTYPE:
The physical appearance "outward, physical manifestation" of an individual on the basis of inherent traits are called as PHENOTYPE.
GENOTYPE:
The genetic makeup of an individual or the entire set of genes in an organism are called as GENOTYPE.