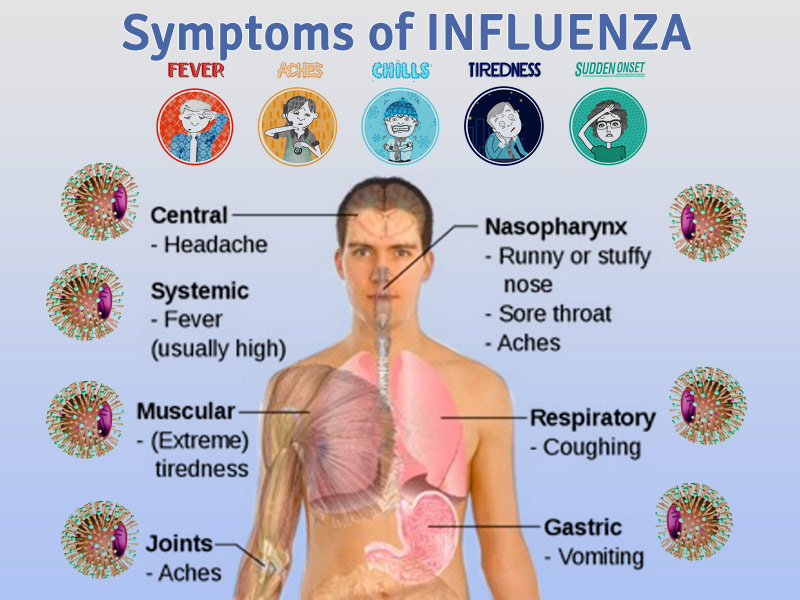
COLOR BLINDNESS:
 |
| HOW IT LOOKS LIKE? |
WHY COLOR BLINDNESS IS MORE COMMON IN MAN?
The reason behind that MALES are more color blind as compared to FEMALES is that the color blind receptor is present on X chromosome.There are two different condition in males and females:COLOR BLINDNESS IN FEMALES:
Two X chromosomes are required from each parents to born a girl.If a girl has to be color blind than she must get two defective X chromosomes from each parent i.e one color blind X from her father and other from her mother and the chances for this type of transfer is often very low that both the parents have defected X chromosomes and if a girl get one defective X and one normal X than the normal chromosomes makes the defective one and she will not become Color Blind.
COLOR BLINDNESS IN MALES:
On the other hand one X and one Y chromosome is required to born a boy i.e X from his mother and Y from his father because women does not have Y chromosome.Now if a boy get defective X from his mother no matter if he gets normal Y from his father he will become color blind because males get only one X chromosome from mothers and he does not get another normal X chromosome which makes the defective one normal.
The color blindness in man totally depends upon what kind of X chromosome they get from their mothers as i have told you that the color blind receptors are present on X chromosomes if they get a defective chromosome than they will become color blind and if they get a normal one then nothing will happen.
NOTE: The Female who has one defective X gene is called Carrier.
This is the basic reason that why color blindness is more common in Males as compared to females.
COLOR BLIND TEST
Look onto this picture and try to recognize the numbers written in the colorful circles
 |
| WHAT DO YOU SEE?? |